When I first encountered the issue of Fast Startup Mode missing from Power Options in Windows 11, it was quite frustrating. The Fast Startup feature, which allows for quicker boot times by saving the system state to a hibernation file, had been a valuable asset on my previous installations of Windows. I had grown accustomed to the speedy boot times it provided and was surprised when I noticed that this option had mysteriously disappeared from my Power Options settings. I decided to investigate and find a solution.
My initial approach was to explore the typical settings and configuration options within Windows 11 to see if I could re-enable Fast Startup through the usual channels. I navigated to the Control Panel, where Power Options are typically configured. To my dismay, I found that the Fast Startup option was not available under the “Choose what the power buttons do” settings. This was puzzling because, on Windows 10, the option was always visible and easily accessible.
Determined to resolve this issue, I started by checking if my system configuration or power settings might have been altered. I accessed the System Settings and examined the Power & Battery settings under the System category. Although these settings provided various power management options, there was no sign of Fast Startup. This led me to suspect that there might be an issue related to system updates or changes in default settings in Windows 11.
Next, I turned my attention to the Group Policy Editor and the Registry Editor, tools I had used previously for system customizations. I started with the Group Policy Editor. I opened the Run dialog by pressing Win + R, typed `gpedit.msc`, and hit Enter. I navigated to `Computer Configuration -> Administrative Templates -> System -> Shutdown`, and looked for any settings related to Fast Startup. However, I found no relevant settings that might affect the visibility of Fast Startup in the Power Options menu.
Not giving up, I moved on to the Registry Editor. I opened the Run dialog again, typed `regedit`, and pressed Enter. I browsed to `HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Session Manager\Power` and looked for a value named `HiberbootEnabled`. The presence and value of this registry key can influence the availability of Fast Startup. However, this registry key was also set correctly and did not seem to be the issue.
Realizing that my attempts through these usual avenues were not fruitful, I decided to look into more specific aspects related to system hardware and updates. It occurred to me that Fast Startup might be impacted by certain hardware or driver configurations. I ensured that all my drivers were up to date, particularly those related to the motherboard and chipset, as these can sometimes affect power management features.
I also considered the possibility that recent Windows updates might have altered or removed the Fast Startup feature in some scenarios. I went through recent Windows updates and verified if any major changes were implemented that might affect power settings. To do this, I accessed the Windows Update settings and reviewed the update history. While nothing specific about Fast Startup was mentioned, I made sure my system was up to date with all recommended updates.
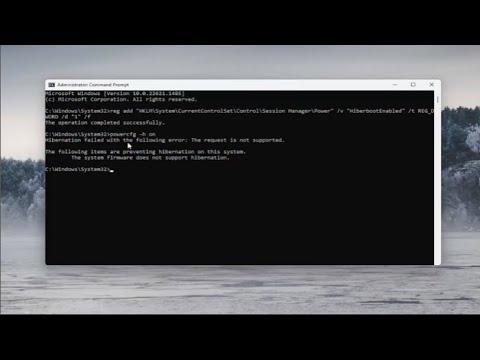
In my research, I stumbled upon a possible link between the issue and the system’s hibernation settings. Fast Startup relies on the hibernation file to function, and if hibernation is disabled, Fast Startup may also be unavailable. To check and enable hibernation, I used the Command Prompt with administrative privileges. I opened the Command Prompt by searching for `cmd` and selecting “Run as administrator.” I then executed the command `powercfg /hibernate on`. This command re-enabled hibernation on my system, which might restore the Fast Startup option.
After executing the command, I returned to the Power Options settings to check if the Fast Startup option had reappeared. Unfortunately, it still did not show up. This led me to consider that there might be additional system configurations or settings that needed adjustment. I checked the BIOS/UEFI settings of my system, as sometimes power-related features are controlled at the hardware level. I rebooted my computer and accessed the BIOS/UEFI setup. I looked through the power management options but found nothing that specifically addressed Fast Startup.
At this point, I decided to perform a more comprehensive approach by checking for any potential system corruption or issues that might be preventing the correct display of Fast Startup. I ran the System File Checker tool by executing `sfc /scannow` in the Command Prompt. This tool scans for and repairs corrupted system files, which could potentially impact system functionalities like Fast Startup.
Following the completion of the scan and repair process, I restarted my computer and revisited the Power Options settings. Still no Fast Startup option appeared. It became clear that the issue might be deeper, possibly involving a more intricate system configuration or a unique interaction with Windows 11 features.
Ultimately, my persistent troubleshooting led me to consult with Windows support forums and tech communities where I found similar experiences shared by other users. Many had encountered the same issue and found that performing a clean installation of Windows 11 often resolved such problems by resetting all system settings to their default states and ensuring that all features were correctly enabled.
Deciding to proceed with a clean installation was a significant step, but it ultimately proved to be the solution. After reinstalling Windows 11, the Fast Startup option reappeared in the Power Options settings, confirming that the issue had been resolved. This experience highlighted the importance of thorough troubleshooting and the potential need for more drastic measures when dealing with elusive system issues.