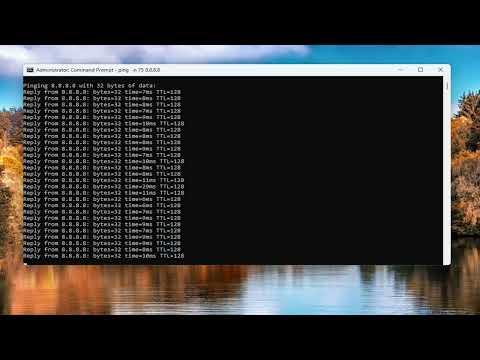
To find packet loss on Windows 11/10, start by opening Command Prompt. You can do this by pressing `Win + R`, typing `cmd`, and hitting Enter. In the Command Prompt window, you’ll use the `ping` and `tracert` commands to diagnose packet loss. Begin with `ping`, which sends packets to a specified IP address or domain and measures how long it takes for them to return. For example, type `ping google.com` and press Enter. The results will show you if there are any packet losses and how long it takes for packets to travel to Google and back.
If you see a high percentage of packet loss or unusually high latency, it suggests there might be an issue with your network connection. To further delve into the problem, use the `tracert` command. This command traces the path packets take to reach a specific destination and can help identify where packet loss occurs. Type `tracert google.com` and hit Enter. This will show you each hop between your computer and the destination. Look for any hops that have high latency or packet loss, as these could indicate network issues.
For a more detailed analysis, you might want to use additional network diagnostic tools. Tools like Wireshark can capture and analyze network traffic, providing deeper insights into where packet loss might be occurring. You would need to download and install Wireshark, then start a capture session. As packets are captured, you can analyze them for any loss or errors.
If you suspect the issue might be with your hardware, such as your router or modem, try restarting these devices. Sometimes, packet loss can be caused by temporary issues with your networking hardware. Additionally, ensure that your network drivers are up-to-date. Go to Device Manager by pressing `Win + X` and selecting `Device Manager`, then expand the Network adapters section. Right-click on your network adapter and select `Update driver`.
In some cases, packet loss can be caused by network congestion or interference, particularly on Wi-Fi networks. If you’re using Wi-Fi, try switching to a wired connection to see if that resolves the issue. If the problem persists, you may want to contact your Internet Service Provider (ISP) for assistance. They can run diagnostics on their end and help you determine if there are issues with your connection.
Lastly, check for any software or applications running on your computer that might be affecting your network performance. Some applications can consume a lot of bandwidth and cause packet loss. Closing unnecessary applications or limiting their bandwidth usage might improve your network stability.
By following these steps, you should be able to identify and address packet loss issues on your Windows 11/10 system.