It was a typical Tuesday morning when I found myself in an unusual predicament. My computer, running Windows XP, was acting up, and I needed to perform a task that required administrative privileges. I had heard that running Command Prompt as an administrator could solve my issues, but I was unsure how to execute this in Windows XP.
Having spent countless hours tinkering with various system settings over the years, I felt somewhat confident navigating the operating system. Yet, the need to run Command Prompt as an administrator had never come up before. As I stared at my screen, I realized that this seemingly simple task required a clear understanding of the specific steps involved, especially considering the unique aspects of Windows XP. Determined to figure it out, I began my quest to delve into the details of running Command Prompt with administrative rights.
First, I had to grasp why running Command Prompt as an administrator was necessary. In Windows XP, certain commands and operations require elevated privileges to execute properly. This administrative level access allows the system to perform tasks that affect system files, settings, and overall configuration, which are restricted to prevent unauthorized changes. This meant that without these elevated privileges, many critical commands and operations would be inaccessible to me, potentially leaving my computer in its troubled state.
To tackle this issue, I needed to follow specific steps to run Command Prompt as an administrator in Windows XP. Unlike more recent versions of Windows, Windows XP does not have a straightforward “Run as administrator” option available directly from the context menu. Instead, the process involves accessing Command Prompt through the right channels, which is a bit more indirect but still manageable with the right approach.
I started by clicking on the “Start” menu located at the bottom-left corner of the screen. From there, I navigated to “All Programs,” then “Accessories.” In this list, I found “Command Prompt,” but I knew that clicking on it normally would not give me the elevated privileges I needed. Instead, I had to take a different route.
The key to running Command Prompt as an administrator in Windows XP was to utilize the “Run” dialog box to initiate the process. I clicked on “Start” again and then selected “Run” from the menu. In the Run dialog box that appeared, I typed “cmd” and then hit Enter. This would open Command Prompt, but again, without the elevated privileges required.
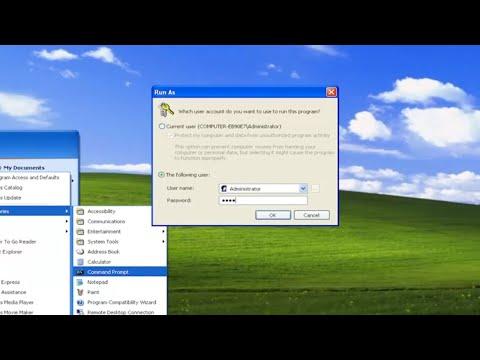
To bypass this, I needed to adjust my approach slightly. I searched for ways to run Command Prompt with administrative rights in Windows XP and discovered that using the built-in Administrator account provided a solution. Windows XP Professional editions come with a hidden Administrator account that has full administrative rights. Enabling and using this account was my ultimate solution.
I returned to the “Run” dialog box and typed “control userpasswords2” and pressed Enter. This action opened the User Accounts window where I could manage different user accounts on the system. From here, I clicked on “Advanced” tab and then “Advanced User Management.” This took me to the Local Users and Groups window, where I could manage user accounts more comprehensively.
Within the Local Users and Groups window, I selected “Users” and looked for the “Administrator” account. By default, this account might be disabled or hidden from the login screen. To enable it, I right-clicked on the “Administrator” account and chose “Properties.” In the Properties window, I unchecked the option “Account is disabled” and applied the changes.
After enabling the Administrator account, I logged out of my current user account and then logged in using the Administrator account. With this account active, I now had full administrative privileges. I could then proceed to open Command Prompt with the necessary rights by clicking on “Start,” then “Run,” typing “cmd,” and hitting Enter. This time, Command Prompt opened with elevated privileges, allowing me to execute the commands and operations required.
This approach to running Command Prompt as an administrator in Windows XP required me to delve into system settings that were not immediately obvious. By leveraging the hidden Administrator account, I achieved the necessary administrative access to address my computer’s issues effectively.
In conclusion, despite the seemingly complex nature of the task, I managed to solve my problem by understanding the unique requirements of Windows XP and utilizing the available tools and settings. Running Command Prompt as an administrator, while not as straightforward in Windows XP as in later versions, was ultimately achievable through these steps. This experience reinforced my understanding of Windows XP’s administrative functions and provided me with a valuable solution for future reference.