I had always prided myself on keeping my computer in top shape, but recently, I started noticing something odd. My internet speed seemed to be unusually slow, and my network usage was off the charts, despite me not actively using the internet. As a tech enthusiast, I was curious to figure out what was causing this sudden spike in network activity. After some research, I discovered that the culprit was the “Service Host: Delivery Optimization” process in Windows 10, which had continued its aggressive network usage even when I wasn’t actively downloading or updating anything. This was a problem I had to address quickly to regain control over my network performance.
Delivery Optimization is a feature in Windows 10 and 11 designed to improve the delivery of updates by allowing your PC to share update files with other computers on the internet. While this is meant to reduce the load on Microsoft’s servers and potentially speed up the update process for everyone, it can also cause significant network congestion if not managed properly. In my case, it was consuming an unreasonable amount of bandwidth and affecting my overall internet experience.
The first step I took to resolve the issue was to dive into the settings where Delivery Optimization could be controlled. I accessed the Windows Settings by clicking on the Start Menu and then selecting the gear icon to open Settings. From there, I navigated to “Update & Security,” where I found the “Windows Update” section. Inside this section, there was an option labeled “Advanced options,” which led me to the “Delivery Optimization” settings.
In the Delivery Optimization settings, I saw an option to turn off the feature entirely or adjust its settings. I decided to start by turning off the option that allowed my PC to upload updates to other PCs on the internet. This was a crucial step, as it immediately stopped my computer from sharing update files, which seemed to be the main source of the high network usage. To do this, I toggled off the option labeled “Allow downloads from other PCs.”
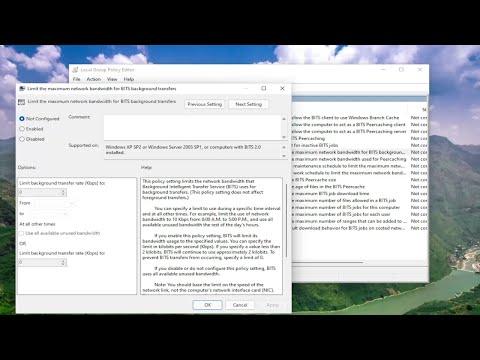
However, turning off this option alone wasn’t enough. I also needed to address the potential impact of Delivery Optimization on my network performance in the future. To do this, I clicked on the “Advanced options” link within the Delivery Optimization settings. Here, I found more granular controls, including the ability to limit the bandwidth used for downloading and uploading updates. I adjusted these settings to limit the amount of bandwidth used, which seemed like a reasonable compromise between keeping Delivery Optimization functional and preventing it from consuming excessive network resources.
Next, I wanted to ensure that these changes were effectively implemented and that there were no lingering issues. To check this, I used the Task Manager to monitor network usage. I accessed the Task Manager by right-clicking on the taskbar and selecting “Task Manager” from the context menu. In the Task Manager, I navigated to the “Performance” tab and selected “Ethernet” or “Wi-Fi” (depending on my connection type) to observe network activity.
Seeing that network usage had significantly decreased, I was cautiously optimistic but wanted to be thorough. I also performed a full system scan to ensure that there were no underlying issues contributing to the high network usage. I ran the built-in Windows Defender antivirus tool, which thoroughly scanned my system for potential threats or issues that might affect network performance.
In addition to these steps, I took the time to review other potential network-consuming applications and services running on my computer. I made sure that there were no background processes or applications that might have been contributing to the high network usage. This included checking for any software updates, running background applications, or other services that might have been consuming bandwidth.
Having made these adjustments, I noticed a significant improvement in my network performance. The aggressive network usage by Service Host: Delivery Optimization was now under control, and my internet speed was back to normal. This experience taught me the importance of understanding and managing system processes that can impact network performance. It also highlighted the value of regularly monitoring and adjusting settings to ensure optimal performance and a smooth computing experience.
In conclusion, addressing the issue of high network usage caused by Service Host: Delivery Optimization in Windows 10 and 11 involves a few key steps. By accessing the Delivery Optimization settings, turning off the option to upload updates to other PCs, and adjusting bandwidth usage limits, I was able to regain control over my network performance. Monitoring network activity through Task Manager and performing a system scan further ensured that there were no other contributing factors. With these measures in place, I was able to restore my internet speed and enjoy a more stable and efficient computing experience.